Treatment for Gynecomastia in Men : Liposuction Alone vs. Liposuction with Subcutaneous Mastectomy – Which Is Better?
Gynecomastia is a benign enlargement of male breast tissue and affects approximately 30% of adolescent males. Although the condition is not medically dangerous, it can have a significant psychological impact, including low self-esteem, negative body image, and emotional distress.
Understanding Gynecomastia in Men
Gynecomastia is a condition caused by an imbalance between the hormones estrogen and testosterone. This hormonal disruption leads to hypertrophy, or the enlargement of male breast gland tissue. In some cases, it may also be accompanied by an excessive accumulation of fat in the chest area.
Gynecomastia is commonly classified into four grades:
- Grade I: Mild breast enlargement without excess skin
- Grade IIa: Moderate breast enlargement without excess skin
- Grade IIb: Moderate enlargement with minor excess skin
- Grade III: Significant enlargement with noticeable excess skin
In mild or early-stage cases, the condition may resolve on its own or respond to hormonal therapy. However, in chronic or more severe cases, surgery remains the most definitive and effective treatment option.
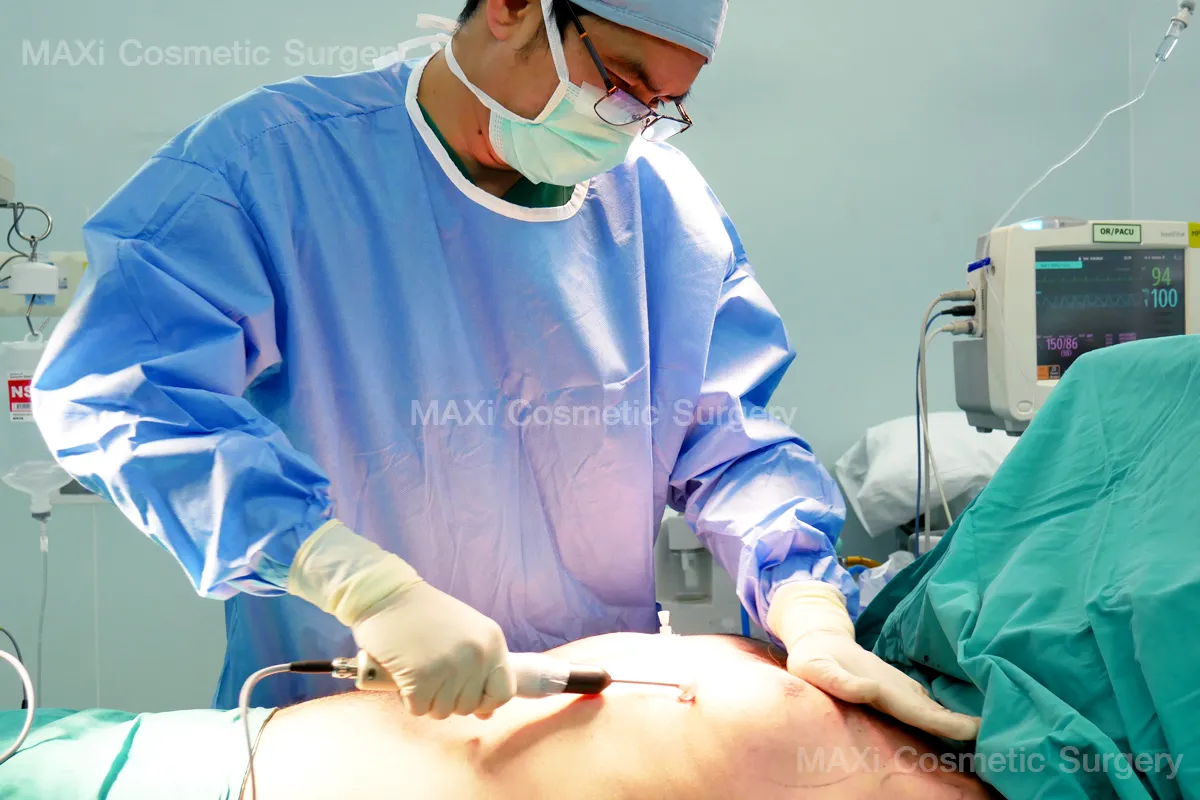
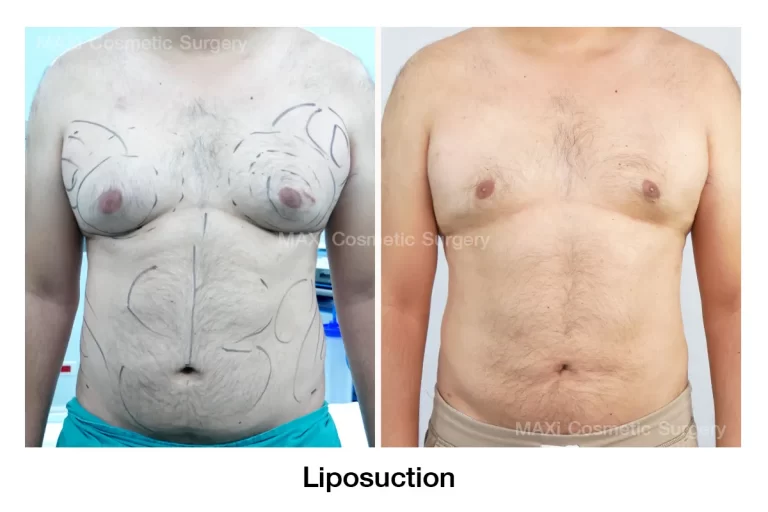
1.Liposuction Only
Best suited for :
- Individuals with Grade I or IIa gynecomastia, where glandular tissue is minimal
- Cases of pseudogynecomastia (breast enlargement primarily due to excess fat)
- Patients without firm glandular tissue or noticeable lumps beneath the nipples
- Those with good skin elasticity
Advantages :
- Small incisions (3–5 mm) and quick recovery time
- Minimal complications, such as bleeding or visible scarring
- Often performed as an outpatient procedure with no need for hospital stay
Limitations :
- Cannot remove firm glandular tissue
- In cases with a significant amount of glandular tissue, there may be residual puffiness around the nipple after surgery
If the patient’s skin lacks elasticity, there is a risk of loose or sagging skin following liposuction
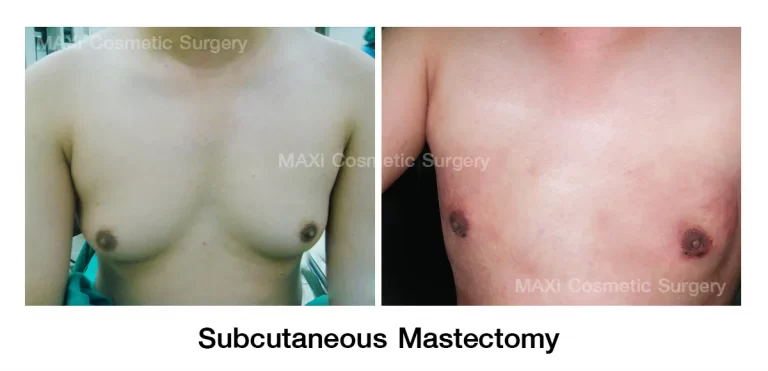
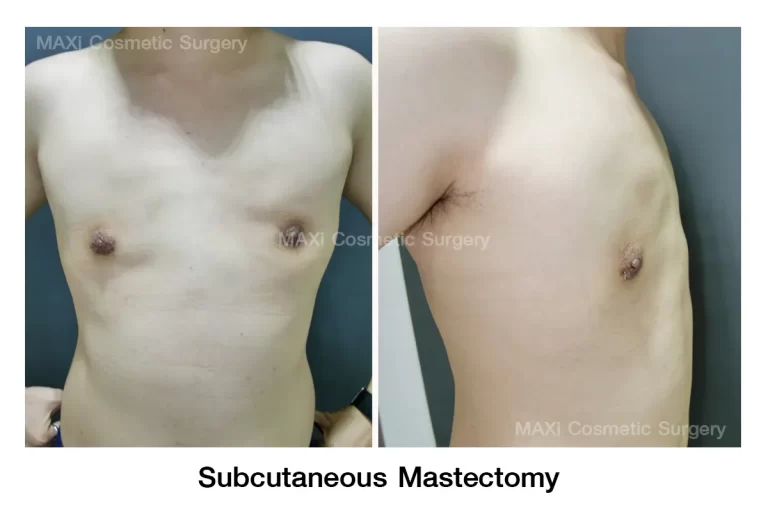
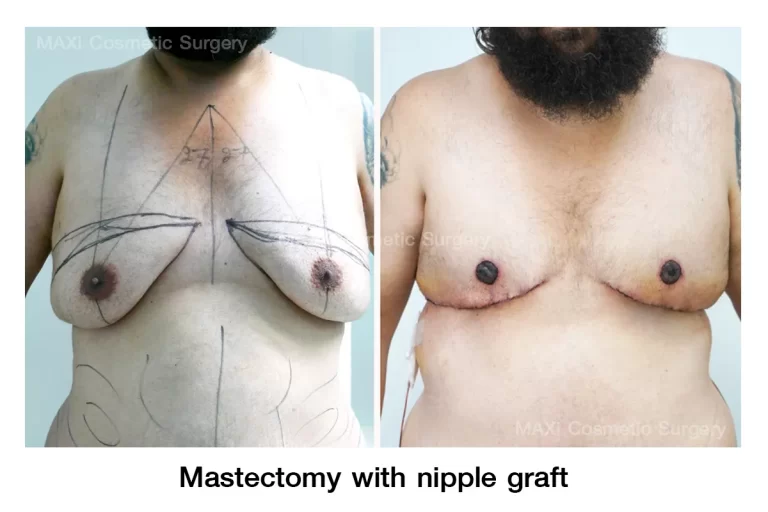
2.Liposuction Combined with Subcutaneous Mastectomy
Best suited for :
- Patients with large or firm glandular breast tissue
- Individuals with visible nipple protrusion
- Those seeking a permanent solution and a smooth, contoured chest appearance
Surgical Techniques :
- Periareolar Subcutaneous Mastectomy: An incision is made around the edge of the areola to access and remove the glandular breast tissue.
- Pull-through Technique: A small incision is made beneath the breast, through which the glandular tissue is extracted—this avoids scarring around the nipple.
- Endoscopic-assisted Technique (in selected cases): A minimally invasive approach using an endoscope to reduce visible scarring.
Advantages :
- Removes both fatty tissue and glandular tissue
- Reduces the risk of recurrence
- Provides a more defined and symmetrical chest contour
Limitations :
- Slightly larger incisions, typically around the areola or under the breast fold
- Slightly longer recovery time compared to liposuction alone
- Risk of scarring or altered nipple sensation in some cases
How to Choose the Right Surgical Approach :
The most suitable technique depends on the type of tissue involved, the severity of the condition, and the patient’s expectations. General guidelines include:
- Fat-dominant gynecomastia ➜ Liposuction alone may be sufficient
- Gland-dominant gynecomastia ➜ Glandular excision should be performed
- Significant skin laxity ➜ May require additional skin excision (e.g., crescent lift, mastopexy)
It is essential to consult with a board-certified plastic surgeon to develop a safe and customized surgical plan that meets your aesthetic goals effectively.
 Thai
Thai